Modules overview¶
Robot module¶

The robot module includes:
Franka Emika Robot arm:. The collaborative arm features 7 DOF with torque sensors at each joint, pose repeatability of +/- 0.1 mm and negligible path deviation even at high velocities. It’s maximum payload is 3 kg, the maximum reach is 855 mm and the workspace coverage is 94.5%.
Franka control: The power interface for controlling the robot, it features and ethernet connection, through which it communicates with the computers, running proprietary controllers.
Control computer: This linux computer is in charge of running the franka_ros interface, enabling ROS integration and custom controllers for the robot.
Pneumatic distro block + raspberry Pi: This solenoid valve pneumatic distribution block, in combination with the raspberry Pi allows for the use of pneumatic tooling with the robot. The raspberry Pi is running a ROS node, capable of adressing individual GPIO pins via ROS service calls. This is mostly used for pneumatic or vacuum grippers and toolchanging.
The computer included in the module is running FCI, an interface allowing for low-level programming and control schemes, providing the current status of the robot and enabling direct torque control at a 1 kHz refresh-rate . On top of the libfranka C++ interface, there are capabilities for integration with the most popular ecosystems, such as ROS, ROS 2 and MATLAB & Simulink.
Vise Module¶
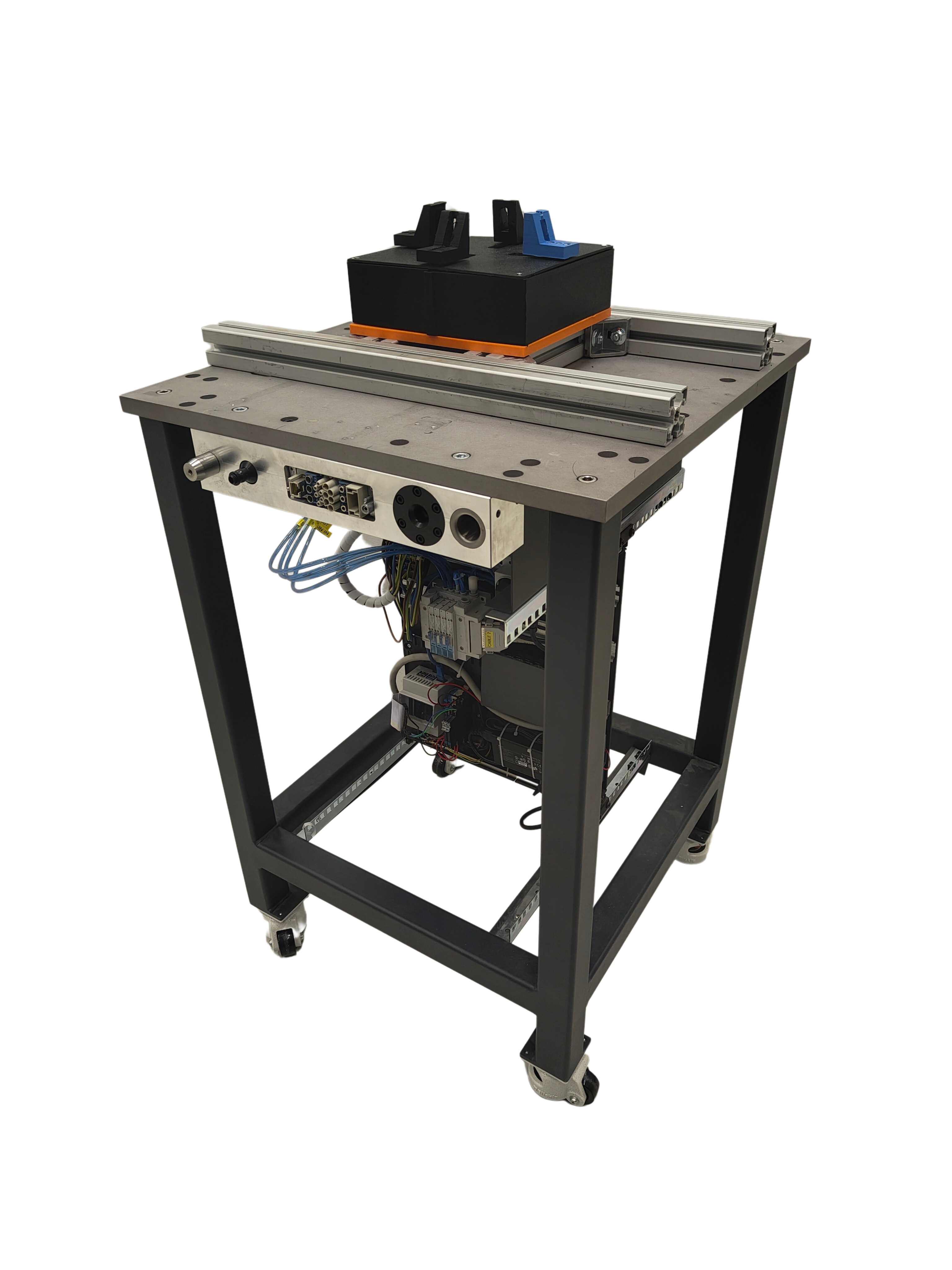

The overall design of the vise was made with adaptability to different workpieces in mind. Externally, the vise is a simple housing with four sliding jaws. Internally, a system of linear guides and actuators, along with the control system located in the module’s drawer, ensures that one face of the workpiece is repeatably in the same position in the vise.
The system does not use encoders. Instead, simple directional pneumatic 5/3 valves control the motion. The vise operates by synchronizing the movement of two opposing jaws using independent flow dampers. The pneumatic system’s inherent property ensures pressure equilibrium across all parts, moving towards the midpoint with equal but opposing forces. This system is less precise than systems using proportional pneumatic valves with position encoders, but this does not pose a problem for the disassembly procedure. Devices entering the process are often imprecise, requiring computer vision to correct positioning inaccuracies.
Cutter Module¶
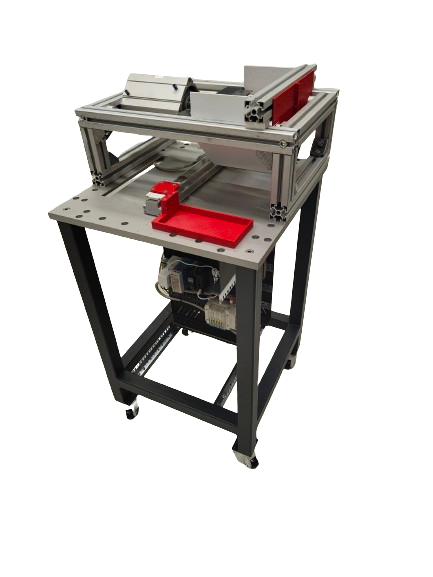
The cutter module is a critical component of the ReconCycle workcell, designed to remove batteries from the heat cost allocator PCB while keeping the batteries undamaged. The workcell’s adaptability allows it to disassemble various types of devices within the same family and entirely different device types. Each device has a unique casing, different PCB layouts, and varying battery locations, shapes, and sizes. This necessitates an adaptable process for this step.
The cutter module performs its task by cutting away the PCB near the battery, a small but acceptable portion of the PCB remains attached to the battery while the rest is disposed of. Some devices require a single cut, while others may need two or three cuts to completely separate the battery. The robot lowers the PCB/battery assembly into the cutting chamber, the blade lowers and the separated battery and PCB parts slide down the hopper into the slideout tray. The trey slides out from underneath the cutter with batteries and debris ready to be sorted by the robot. Despite its apparent simplicity, several issues need to be addressed for an effective cutting process.
The cutter, is designed to handle a wide variety of PCB/battery combinations. The frame is made of aluminium extrusion, featuring linear guides for the blade and a fixed cutting surface. A pneumatic cylinder at the top of the frame provides the necessary cutting force. The blade is housed behind a protective transparent plastic cover at the front, to contain the shrapnel, while still providing a sufficiently wide workspace for robot access in different configurations.
Attached to the pneumatic cylinder is a hardened steel blade capable of cutting through tough PCB composite, metal conductors, and other PCB parts. An adjustable end-stop behind the blade ensures precise insertion of the PCB/battery assembly, allowing for accurate and repeatable cutting and a minimal ammount of PCB left attached to the battery.
CNC Module¶
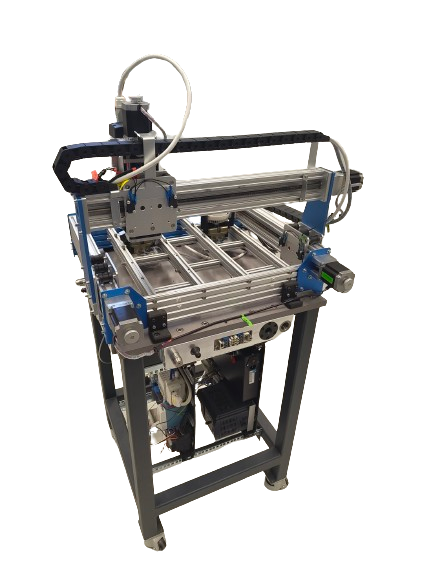
The CNC module is used for smoke-detector disassembly, due to the wide variety of different smoke detectors that have to be processed, this was the most robust solution. The module contains:
: This CNC router was selected for closely matching the dimensions of a robot module, while maximising the work area. It features 400 x 300 mm of working area, it’s been upgraded with an internal frame made of aluminium extrusion, to improve it’s rigidity and a 3-phase spindle, controlled by a variable frequency drive (VFD).
Pneumatic grippers: Mounted to the axtruded aluminium frame are 2
pneumatic centric grippers. These are used for workholding of the smoke detectors when carving, they feature custom, replaceable 3D-printed jaws, allowing for quick adaptation to different smoke-detectors. The grippers can have the stroke speed and clampoing force adjusted via in-line flow dampers and pressure regulators respectively.
Pneumatic distro block + raspberry Pi: The combination of the Raspberry Pi single-board computer (SBC) and the distro block allows for controll of the grippers via ROS service calls. Additionaly, the Raspberry Pi communicates with the CNC’s controller through a USB connection, allowing for CNC operation via ROS action server.
Vision Module¶
The vision module plays double duty as the infeed module. The disassembly process starts with the workpiece on the vision table, where it’s detected and classified. Further dissasembly steps are based on this detection ad classification, as they are specific to the device type. The module features a , mounted above the table, which is in charge of the workpiece detection and classification.